In today’s fast-paced financial landscape, managing your hard-earned money can feel overwhelming. Market volatility, inflation, and unexpected life events can threaten even the most carefully planned savings—but what if you could turn uncertainty into opportunity? Consumer portfolio management isn’t just for Wall Street experts; it’s a practical skill that empowers everyday individuals to take control of their financial futures. Whether you’re saving for retirement, a child’s education, or simply aiming to grow your wealth, the principles of diversification, risk management, and strategic growth can transform how you approach your assets.
Think of your portfolio as a garden: without proper care, some plants might wither, while others could overcrowd the space. Diversifying your investments—like planting a mix of crops—ensures that no single market downturn or sector crash devastates your financial health. Protecting your assets through tools like emergency funds, insurance, and tax-efficient strategies acts as a safety net, shielding you from life’s storms. Meanwhile, nurturing growth through compound interest, dividend reinvestment, and smart exposure to trends (like tech or renewable energy) helps your wealth flourish over time.
But where do you start? This guide breaks down the essentials of consumer portfolio management into actionable steps. You’ll learn how to balance risk and reward, leverage modern tools like robo-advisors and ETFs, and avoid common pitfalls like emotional investing or overconcentration. From building a resilient investment mix to optimizing retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs, we’ll walk you through strategies tailored for both beginners and seasoned savers.
Ready to transform your financial future? Let’s dive into the five pillars of effective portfolio management—diversify, protect, grow, manage risk, and harness today’s tools—to build a roadmap that turns your goals into reality. No jargon, no guesswork: just clear, practical advice to help you thrive in any marke
Building a Diversified Investment Portfolio
A diversified investment portfolio acts like a financial safety net, spreading risk across asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) and sectors to avoid catastrophic losses. According to the SEC’s investor guide on diversification, even small investors can minimize volatility by balancing high-growth assets with stable ones. For example, overconcentration in a single stock—like those who held only tech shares during the 2000 dot-com crash—can wipe out years of gains overnight. By mixing domestic and international investments, growth-oriented and defensive assets, you create a resilient portfolio designed to weather market storms.
Why diversification is your first line of defense against risk.
1: Asset Allocation Techniques
(Balancing your portfolio’s “ingredients” for stability and growth.)
- Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT): Explain Harry Markowitz’s Nobel-winning framework: balancing high-risk/high-reward assets (stocks) with stable ones (bonds) to maximize returns for a given risk level.
- Rule-Based Allocation:
- 60/40 Rule: 60% stocks (growth) + 40% bonds (stability).
- Age-Based Allocation: Subtract your age from 100 to determine stock allocation (e.g., 30 years old = 70% stocks).
- Alternative Assets: Add real estate (REITs), commodities (gold), or cryptocurrencies (1-5% of portfolio) to hedge against market swings.
- Example: A 35-year-old’s portfolio: 65% stocks (50% U.S., 15% international), 25% bonds, 5% REITs, 5% cash.
2: Choosing the Right Investment Vehicles
(Pick tools that match your goals and risk tolerance.)
- ETFs vs. Mutual Funds:
- ETFs: Low-cost, tax-efficient, and tradable like stocks (e.g., SPDR S&P 500 ETF).
- Mutual Funds: Actively managed, higher fees, but potential for outperformance (e.g., Fidelity Contrafund).
- Index Funds: Mimic benchmarks like the S&P 500 (e.g., Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund).
- Sector-Specific Stocks: Tech (Apple), healthcare (Johnson & Johnson), or renewable energy (NextEra Energy) for targeted growth.
- Bonds: Treasury bonds (safety) vs. corporate bonds (higher yield, e.g., Microsoft bonds).
3: Avoiding Overconcentration
(Don’t put all your eggs in one basket—lessons from history.)
- Case Study: 2008 Housing Crash: Investors overexposed to real estate or bank stocks lost 50%+ of their portfolios.
- Red Flags:
- A single stock >10% of your portfolio.
- Overinvesting in your employer’s stock (e.g., Enron collapse).
- Fix It: Trim oversized positions gradually and reinvest in underrepresented assets.
- Warren Buffett Wisdom: “Diversification is protection against ignorance. It makes little sense if you know what you’re doing.” (But most consumers aren’t experts!)
4: Global Diversification
(Expand beyond your home country’s borders.)
- Why It Matters: The U.S. is only 60% of global market cap—ignoring international markets misses opportunities.
- Emerging Markets: Higher growth (e.g., India, Vietnam) but higher volatility. Use ETFs like iShares MSCI Emerging Markets.
- Developed Markets: Stability from Europe (e.g., Vanguard FTSE Europe ETF) or Japan (iShares MSCI Japan ETF).
- Currency Risk: Hedge with funds that hold foreign currencies or multinational corporations (e.g., Nestlé, Samsung).
Key Takeaways for Readers
- Start Simple: Use a target-date fund or robo-advisor (e.g., Betterment) for automatic diversification.
- Rebalance Annually: Adjust allocations to stay aligned with your goals.
- Think Long-Term: Diversification smooths out short-term volatility but requires patience.
Protecting Your Assets from Market Volatility and Risks
Strategies to safeguard your wealth during uncertain times.
1: Emergency Fund Planning
Your financial shock absorber.
- Why It’s Critical:
- An emergency fund prevents you from liquidating investments at a loss during crises (e.g., job loss, medical emergencies).
- Studies show 40% of Americans can’t cover a $400 emergency—don’t be part of that statistic.
- How Much to Save:
- 3-6 months of expenses: Adjust based on risk factors (e.g., freelancers: 9-12 months).
- Calculate using tools like Mint or Personal Capital.
- Where to Park It:
- High-yield savings accounts (e.g., Ally Bank, 4%+ APY).
- Money market accounts or short-term Treasury bills for liquidity and modest growth.
- Case Study:
During the 2020 pandemic, individuals with emergency funds avoided tapping into retirement accounts (and penalties) to cover expenses.
2: Insurance as a Safety Net
Mitigate personal and financial risks.
- Types of Insurance:
- Health Insurance: Avoid catastrophic medical debt (average U.S. emergency room visit: $1,500+).
- Term Life Insurance: Affordable coverage for dependents (e.g., 20-year term policy for $30/month).
- Property Insurance: Protects against disasters (e.g., wildfires, floods).
- Disability Insurance: Replaces income if you can’t work (1 in 4 workers will face a disability).
- Umbrella Policies:
- Extra liability coverage (e.g., $1 million policy) for lawsuits or accidents.
- Pro Tip:
Review policies annually—life changes (marriage, kids, new home) require adjustments.
3: Hedging Strategies
Offset losses with defensive assets.
- Gold and Precious Metals:
- Historically rise during inflation (e.g., gold surged 25% in 2022 amid rising prices).
- ETFs like SPDR Gold Shares (GLD) offer easy exposure.
- Bonds as Ballast:
- Treasury bonds (safe haven) and corporate bonds (higher yield) balance equity volatility.
- Example: In 2008, long-term Treasuries gained 25% while stocks crashed.
- Inverse ETFs:
- Bet against market declines (e.g., ProShares Short S&P 500 (SH)).
- Use sparingly—complex and costly for long-term holds.
- Diversify with Defensive Stocks:
- Utilities (NextEra Energy) and consumer staples (Procter & Gamble) thrive in downturns.
4: Tax-Efficient Investing
Keep more of what you earn.
- Tax-Advantaged Accounts:
- Roth IRA: Tax-free growth (ideal for young investors in lower tax brackets).
- 401(k): Employer matches are “free money” (contribute enough to max the match).
- HSAs: Triple tax benefits (deductible contributions, tax-free growth, tax-free withdrawals for medical costs).
- Municipal Bonds:
- Tax-free interest (e.g., Vanguard Tax-Exempt Bond ETF (VTEB)).
- Tax-Loss Harvesting:
- Offset capital gains by selling losing investments (e.g., sell a tech stock down 20% to balance gains elsewhere).
- Tools like Wealthfront automate this process.
- Case Study:
A $10,000 investment in a taxable account vs. Roth IRA over 30 years (7% return): Taxable account = ~$57,000 after capital gains tax. Roth IRA = $76,000 tax-free.
5: Behavioral Strategies to Avoid Panic Selling
Master your mindset to protect your portfolio.
- Common Pitfalls:
- Recency Bias: Overreacting to short-term dips (e.g., selling during March 2020’s COVID crash).
- FOMO: Chasing meme stocks or crypto hype (e.g., GameStop, Dogecoin).
- Solutions:
- Set a long-term plan and stick to it (rebalance annually, ignore daily headlines).
- Automate contributions (dollar-cost averaging reduces emotional decisions).
- Work with a fiduciary advisor to stay disciplined.
- Warren Buffett’s Advice:
“Be fearful when others are greedy, and greedy when others are fearful.”
Key Takeaways for Readers
- Layer Your Protections: Combine emergency funds, insurance, and hedging.
- Optimize Taxes: Use retirement accounts and municipal bonds to shield gains.
- Stay Calm: Volatility is normal—focus on time horizons, not daily swings.
Growing Your Wealth Sustainably
Balancing risk and reward for long-term financial health.
1: The Power of Compound Interest
Let time and reinvestment work for you.
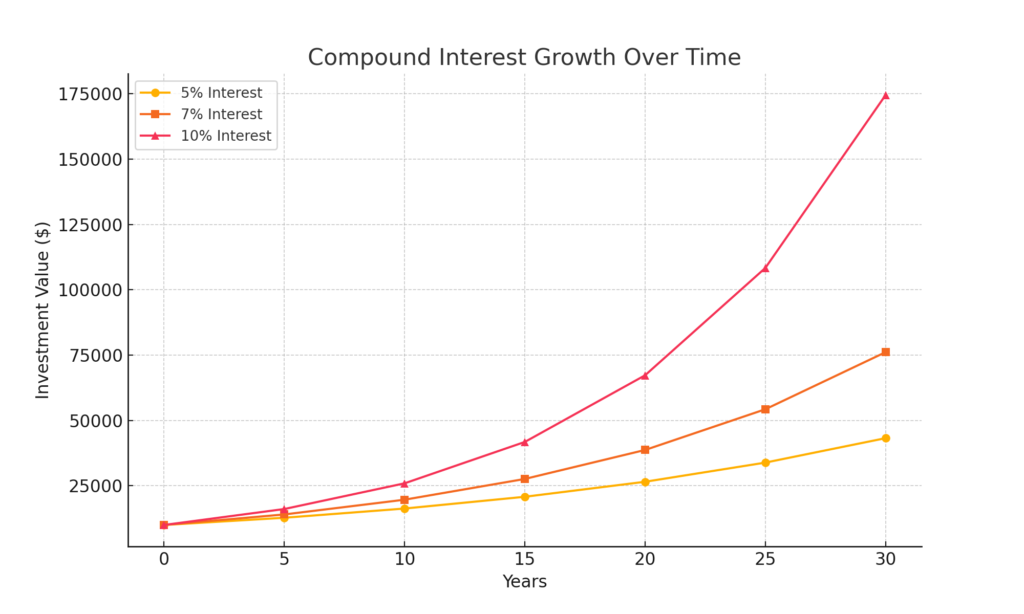
- How It Works:
- Compound interest = earning returns on your initial investment and accumulated interest.
- Formula: A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt) (e.g., $10,000 at 7% annual return becomes $76,123 in 30 years).
- Start Early Advantage:
- A 25-year-old investing $300/month at 7% will have ~$1.2 million by age 65.
- A 35-year-old starting the same plan will have ~$567,000—half the wealth due to 10 fewer years of compounding.
- Reinvest Dividends:
- Example: Procter & Gamble (PG) has raised dividends for 67+ years. Reinvesting dividends could turn $10,000 into $800,000+ over 50 years.
- Tools: Use compound interest calculators (NerdWallet, Bankrate) to visualize growth.
2: Active vs. Passive Investing
Choose a strategy that aligns with your goals and effort.
- Passive Investing:
- Pros: Low fees, minimal effort, mirrors market returns (e.g., S&P 500 ETFs like VOO).
- Cons: No outperformance; “average” returns.
- Example: Warren Buffett’s $1 million bet that an S&P 500 index fund would beat hedge funds over 10 years—it won by 85%.
- Active Investing:
- Pros: Potential to beat the market (e.g., Cathie Wood’s ARKK ETF during tech rallies).
- Cons: Higher fees (1-2% annually), requires research, and emotional discipline.
- Hybrid Approach:
- Core portfolio in index funds (80%) + satellite bets on individual stocks or sectors (20%).
- Robo-Advisors: Platforms like Betterment or Wealthfront automate passive strategies with tax optimization.
3: Leveraging Market Trends Without Chasing Hype
Spot sustainable opportunities, not fleeting fads.
- Mega-Trends:
- Renewable energy (solar ETFs like TAN), AI (Nvidia, Microsoft), and aging populations (healthcare ETFs like XLV).
- Why It Works: These sectors have long-term tailwinds vs. short-term hype (e.g., meme stocks).
- Value Investing:
- Buy undervalued companies with strong fundamentals (e.g., Benjamin Graham’s “margin of safety”).
- Example: Apple in 2016 (P/E ratio ~10) vs. 2023 (P/E ~30)—early investors saw 500%+ returns.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA):
- Invest fixed amounts regularly (e.g., $500/month) to smooth out market volatility.
- Case Study: Investing $500/month in Nasdaq (QQQ) during the 2008 crash yielded 15%+ annualized returns by 2023.
4: Sustainable and Ethical Investing (ESG)
Align growth with your values.
- ESG Criteria:
- Environmental: Carbon footprint, renewable energy use (e.g., Tesla, NextEra Energy).
- Social: Labor practices, diversity (e.g., Salesforce’s equal pay initiatives).
- Governance: Board transparency, anti-corruption policies (e.g., Microsoft’s ESG reports).
- ESG Funds:
- ETFs like iShares Global ESG ETF (ESGD) or Vanguard ESG U.S. Stock ETF (ESGV).
- Returns: 75% of ESG funds outperformed peers in 2020 (Morningstar data).
- Impact Investing:
- Direct investments in social enterprises (e.g., green bonds, microfinance).
- Avoid Greenwashing: Research fund holdings—some “ESG” funds still include fossil fuels.
5: Automating Wealth Growth
Set it, forget it, and let systems compound gains.
- Automated Contributions:
- Schedule monthly transfers to investment accounts (e.g., Fidelity, Vanguard).
- Treat it like a bill—pay yourself first.
- Target-Date Funds:
- Automatically adjust stock/bond ratios as you near retirement (e.g., Vanguard Target Retirement 2050).
- Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs):
- Companies like Coca-Cola (KO) let you reinvest dividends to buy more shares commission-free.
- Behavioral Benefits:
- Reduces emotional decisions (e.g., panic-selling) and enforces discipline.
Key Takeaways for Readers
- Start Now: Even small, regular investments compound massively over decades.
- Stay Balanced: Mix passive strategies (index funds) with targeted bets (megatrends, ESG).
- Automate: Remove human error and emotion from the equation.
Managing Risk in Your Portfolio
Align your investments with your risk appetite and financial goals.
1: Risk Tolerance Assessment
Know your financial comfort zone.
- What Is Risk Tolerance?:
Your ability to endure market swings without panic-selling. Factors include age, income stability, and financial goals (e.g., retirement vs. short-term savings). - Tools to Measure It:
- FINRA’s Risk Meter: A free quiz to gauge your risk profile (conservative, moderate, aggressive).
- Vanguard’s Investor Questionnaire: Recommends asset allocations based on your answers.
- Case Study:
A 30-year-old tech worker with stable income might choose 80% stocks/20% bonds, while a 55-year-old nearing retirement opts for 50% stocks/50% bonds. - Behavioral Traps:
- Overconfidence: Young investors taking excessive risks (e.g., 100% crypto).
- Loss Aversion: Older investors hoarding cash and missing growth.
- Pro Tip:
Reassess risk tolerance after major life events (marriage, inheritance, job loss).
2: Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Keep your asset mix aligned with your goals.
- Why Rebalance?:
Market shifts can skew your allocation (e.g., stocks surging to 90% of a 70/30 portfolio). - How to Do It:
- Calendar-Based: Rebalance annually or quarterly.
- Threshold-Based: Act when an asset class deviates by ±5% from its target.
- Example:
In 2021, tech stocks soared. A disciplined investor sold some tech ETFs and bought undervalued bonds to restore their 60/40 split. - Tax Efficiency:
Rebalance in tax-advantaged accounts (e.g., IRAs) to avoid capital gains taxes. - Tools:
Use robo-advisors like Betterment or Wealthfront for automatic rebalancing.
3: Liquidity Management
Ensure you can access cash without derailing long-term plans.
- What Is Liquidity?:
Assets that can be quickly converted to cash without significant loss (e.g., savings accounts, short-term Treasuries). - The 3-Tier Approach:
- Emergency Fund: 3-6 months of expenses in high-yield savings (e.g., Ally Bank).
- Near-Term Goals: Money needed in 1-3 years parked in CDs or bond ladders.
- Long-Term Investments: Stocks/real estate for goals 5+ years away.
- Case Study:
During the 2020 pandemic, investors with liquid cash avoided selling stocks at a 30% loss to cover expenses. - Avoid Illiquid Traps:
Private equity, real estate, or collectibles should be <10% of your portfolio unless you’re a seasoned investor.
4: Understanding Market Benchmarks
Measure performance to avoid costly assumptions.
- Key Benchmarks:
- S&P 500: Tracks 500 large U.S. companies (general market health).
- NASDAQ Composite: Tech-heavy index (e.g., Apple, Amazon).
- Bloomberg Aggregate Bond Index: Measures the bond market.
- Track Your Portfolio’s “Tracking Error”:
If your portfolio consistently lags the S&P 500, consider shifting to low-cost index funds. - Example:
An investor’s 70% stock/30% bond portfolio returned 6% in 2023, while the S&P 500 gained 24%. This signals over-diversification or poor stock picks. - Tools for Comparison:
Morningstar’s Portfolio Manager or Personal Capital’s Investment Checkup.
Key Takeaways for Readers
- Test Your Risk Tolerance: Use free tools to avoid mismatched investments.
- Rebalance Religiously: Prevent drift and lock in gains.
- Prioritize Liquidity: Protect against emergencies and opportunity costs.
- Benchmark Wisely: Know when to pivot vs. stay the course.
Tools and Strategies for Modern Investors
Leverage technology and psychology to simplify and optimize your portfolio.
1: Robo-Advisors and Budgeting Apps
Automate your finances for efficiency and discipline.
- Top Robo-Advisors:
- Betterment: Offers goal-based portfolios (retirement, travel) with tax-loss harvesting (saves 0.5-1% annually in taxes).
- Wealthfront: Features a high-yield cash account and low-cost ESG portfolios.
- Vanguard Digital Advisor: Combines low fees (0.15%) with Vanguard’s trusted index funds.
- Budgeting Apps:
- Mint: Tracks spending, net worth, and credit score (free, ad-supported).
- You Need a Budget (YNAB): Teaches zero-based budgeting—ideal for debt reduction.
- Personal Capital: Merges budgeting with investment tracking (retirement fee analyzer tool).
- Case Study:
A user investing $10,000 with Wealthfront’s automated rebalancing saved 2 hours/month on portfolio management and avoided emotional trading during the 2022 bear market.
2: Retirement Accounts (401(k), IRA)
Maximize tax advantages for long-term growth.
- 401(k) Essentials:
- Employer Match: Free money! Contribute at least enough to max the match (e.g., 6% salary).
- 2024 Contribution Limits: $23,000 (under 50), $30,500 (over 50).
- Roth vs. Traditional: Roth for tax-free withdrawals (if you expect higher taxes later).
- IRA Strategies:
- Backdoor Roth IRA: For high earners (>$153k single) to bypass income limits.
- SEP IRA: For self-employed individuals (contribute up to 25% of income).
- Example:
Maxing a 401(k) with a $23,000 annual contribution at 7% return grows to ~$2.5 million in 30 years. - Tools:
Use Fidelity’s Retirement Score or Charles Schwab’s IRA Calculator to project savings.
3: Behavioral Finance Tips
Outsmart your brain’s worst investing instincts.
- Common Biases:
- Loss Aversion: Holding losing stocks too long (e.g., refusing to sell Blockbuster in 2008).
- Anchoring: Obsessing over an asset’s past price (e.g., waiting for Bitcoin to “return to $60k”).
- Herding: Following crowds into trends (e.g., meme stocks like AMC).
- Solutions:
- Automate investments (set recurring deposits to avoid timing the market).
- Create an investment policy statement (IPS) outlining your goals, risk tolerance, and rules.
- Use commitment devices: Apps like Acorns round up purchases to invest spare change.
- Expert Insight:
Nobel laureate Daniel Kahneman: “The easiest way to increase happiness is to control your time and avoid daily stock checks.”
4: Staying Compliant with Regulations
Navigate rules to protect your investments.
- Key Regulations:
- SEC’s Regulation Best Interest (Reg BI): Requires brokers like Interactive Brokers to act in clients’ best interest.
- FINRA Rules: Prohibits insider trading and ensures fair pricing.
- Tax Compliance:
- Report capital gains/losses via IRS Form 8949.
- Wash Sale Rule: Don’t rebuy the same stock within 30 days of selling at a loss.
- Resources:
- Investor.gov: SEC’s free site for checking advisor credentials and avoiding scams.
- Morningstar’s Stewardship Grades: Rates funds on regulatory compliance and transparency.
- Case Study:
In 2021, the SEC fined Robinhood $65 million for misleading customers about revenue from payment for order flow—a reminder to vet platforms.
Key Takeaways for Readers
- Automate Wisely: Use robo-advisors for hands-off growth and apps like YNAB for budget discipline.
- Maximize Tax Breaks: Prioritize 401(k) matches and IRA contributions.
- Master Your Mindset: Build rules to counter biases and avoid costly emotional decisions.
- Stay Informed: Follow SEC/FINRA updates to dodge penalties and scams.
Conclusion: Build a Resilient Financial Future—One Step at a Time
Mastering consumer portfolio management means embracing five pillars: diversify to mitigate risk, protect against volatility, grow with discipline, manage risk proactively, and harness modern tools to streamline decisions. Whether you’re investing your first $100 or rebalancing a seasoned portfolio, progress begins with small, consistent actions. Automate contributions, review your strategy annually, and adjust as your goals evolve—wealth-building is a marathon, not a sprint.
Even the most successful investors started somewhere. By staying patient and avoiding impulsive moves, you’ll turn steady habits into compounding rewards. Remember, the market rewards consistency, not perfection.